C# | Difference between == and Equals()
Both the == Operator and the Equals() method are used to compare two value type data items or reference type data items. This article explains the basic difference between these two. The Equality Operator ( ==) is the comparison operator and the Equals() method compares the contents of a string. The == Operator compares the reference identity while the Equals() method compares only contents. Let’s see with some examples.
In the first example, we assigned a string variable to another variable. A string is a reference type and in the following example, a string variable is assigned to another string variable so they are referring to the same identity in the heap and both have the same content so you get True output for both the == Operator and the Equals() method.
using System;
namespace ComparisionExample
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
string name = "sandeep";
string myName = name;
Console.WriteLine("== operator result is {0}", name == myName);
Console.WriteLine("Equals method result is {0}", name.Equals(myName));
Console.ReadKey();
}
}
}
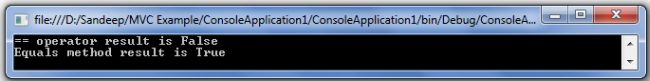
Let’s see another example where the contents will be the same in both object variables but both have different references. So the == Operator returns False because it compares the reference identity while the Equals() method returns True because it compares the contents of the objects.
using System;
namespace ComparisionExample
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
object name = "sandeep";
char[] values = {'s','a','n','d','e','e','p'};
object myName = new string(values);
Console.WriteLine("== operator result is {0}", name == myName);
Console.WriteLine("Equals method result is {0}", myName.Equals(name));
Console.ReadKey();
}
}
}

Comments
Post a Comment